Ronco, widely known as snoring, is a common condition where a person makes a hoarse or harsh sound while sleeping due to the vibration of relaxed tissues in the throat. While it might appear to be a minor inconvenience, ronco can lead to a number of complications, especially if it occurs frequently or is excessively loud.
Snoring is often brushed off as just a sleep disturbance, but it can impact sleep quality, relationships, daily energy levels, and even long-term health. Understanding what ronco is and what causes it is essential for managing or treating it effectively.
The Mechanics Behind Ronco
When you sleep, your body enters a relaxed state. Muscles all over the body loosen—including those in the tongue, throat, and soft palate. In some people, these tissues relax enough to partially block the airway. As air flows through this narrowed space, the tissues vibrate and produce the sound known as Ronco.
The louder the vibration, the louder the snore. This is more likely if the airway is significantly narrowed, or if breathing becomes labored due to nasal congestion or poor sleep posture.
Risk Factors for Developing Ronco
There are various factors that increase the likelihood of ronco, including:
- Age: As people grow older, throat muscles lose tone and become more prone to vibration.
- Obesity: Excess fatty tissue around the neck and throat area can constrict airways.
- Gender: Statistically, men snore more often than women due to narrower air passages.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol relaxes throat muscles, increasing the chance of airway collapse.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke irritates the airway and increases inflammation, worsening ronco.
- Nasal Issues: Chronic congestion, allergies, or a deviated septum can obstruct airflow.
Understanding these risk factors can help in creating a plan to reduce or eliminate snoring.
Common Myths About Ronco
Despite being common, ronco is surrounded by misconceptions. Let’s debunk a few of them:
- Myth: Everyone who snores has sleep apnea
Fact: Not all snorers have sleep apnea. While the two can be related, simple snoring is often benign. - Myth: Snoring is harmless
Fact: Chronic snoring may point to underlying issues and can significantly disrupt sleep patterns. - Myth: Only men snore
Fact: While men are more likely to snore, women also experience ronco, especially after menopause. - Myth: There’s nothing you can do about snoring
Fact: Many lifestyle and medical treatments exist to manage or cure ronco.
Dispelling these myths is important for encouraging people to take ronco seriously and seek help when needed.
How Ronco Affects Daily Life
For those who snore and those who sleep near a snorer, the effects of ronco can ripple into daily routines. These include:
- Sleep Disruption: Snoring can wake both the snorer and their bed partner multiple times per night.
- Daytime Drowsiness: Poor sleep due to snoring can lead to low energy and impaired focus.
- Emotional Stress: Snoring can cause embarrassment or irritability.
- Relationship Strain: Partners often end up sleeping separately or experience reduced sleep satisfaction.
The effects go beyond mere noise—they can influence a person’s quality of life and overall well-being.
Home Remedies to Manage Ronco
For mild cases of snoring, simple adjustments at home can have a significant impact:
- Change Sleeping Position: Sleeping on your side instead of your back can reduce throat collapse.
- Elevate Your Head: Raising the head of your bed or using thicker pillows can help open airways.
- Stay Well Hydrated: Dry throat tissue vibrates more easily; drinking enough water helps.
- Avoid Alcohol at Night: Especially within 3–4 hours before bedtime.
- Use a Humidifier: Dry air can irritate nasal passages and worsen ronco.
- Practice Good Sleep Hygiene: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
These low-effort solutions are often the first line of defense in treating ronco naturally.
When Ronco Is a Sign of a Bigger Problem
Occasional ronco is usually harmless, but chronic snoring can sometimes signal obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)—a more serious sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
Red flags to watch for include:
- Loud, frequent snoring
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Morning headaches
- Extreme daytime sleepiness
- Irritability or mood swings
If any of these signs are present, it’s crucial to seek a medical evaluation. Left untreated, OSA can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, and other chronic health conditions.
Clinical Treatments for Persistent Ronco
If home remedies don’t reduce ronco, several medical treatments may be considered:
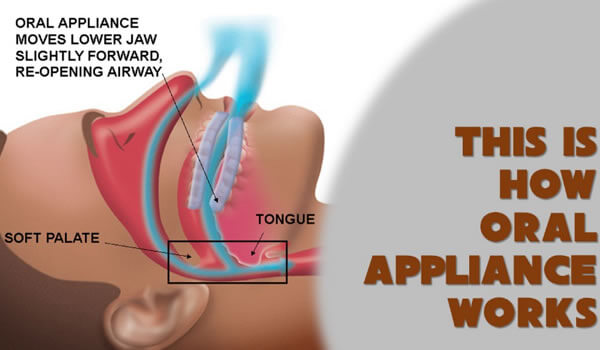
- Oral Devices: These are custom-fitted mouthpieces that keep the airway open by positioning the jaw forward.
- CPAP Machines: Especially for sleep apnea, this device provides constant air pressure to keep the throat open.
- Surgery: Procedures like uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) remove excess tissue that blocks airflow.
- Laser-Assisted Uvuloplasty (LAUP): A less invasive method to reshape throat tissue using lasers.
- Injection Snoreplasty: Injects a substance to harden the soft palate and reduce vibration.
Each method has its own pros and cons, and a sleep specialist can help determine the best path forward.
Ronco in Children: A Hidden Issue
Children can experience ronco too, often due to enlarged tonsils or adenoids, allergies, or nasal obstructions. Pediatric snoring should not be ignored, especially if it leads to:
- Breathing pauses
- Restlessness during sleep
- Bedwetting
- Poor academic performance
- Hyperactivity during the day
Parents should observe nighttime behavior and consult a pediatrician if symptoms persist. Treatment may include allergy management, tonsil removal, or behavioral interventions.
Lifestyle Habits That Help Prevent Ronco
Long-term prevention of ronco often comes down to healthy daily habits:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for snoring.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoke irritates airways and increases the likelihood of tissue vibration.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity strengthens muscles, including those in the throat.
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: A full stomach can push against the diaphragm and affect breathing.
- Sleep on a Firm Mattress: It promotes better posture and airflow during sleep.
Incorporating these habits into your routine may significantly reduce ronco over time.
Living with Ronco: How to Cope
If you or someone you live with has chronic ronco, it’s important to communicate openly and look for solutions together. Coping strategies include:
- Using White Noise: This can mask the sound and help bed partners sleep better.
- Sleeping Separately (Occasionally): Sometimes, a temporary solution like separate beds can preserve peace and rest.
- Keeping a Sleep Diary: Helps identify patterns or triggers.
- Seeking Support: Joining forums or talking to others experiencing similar issues can provide relief.
Understanding, empathy, and a willingness to adapt are key to managing ronco in relationships.
Conclusion
Ronco is more than just a nighttime annoyance—it can affect physical health, emotional well-being, and interpersonal relationships. Although snoring is common, it should not be ignored, especially if it’s frequent or loud. Fortunately, a wide range of home remedies, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions are available to manage and potentially eliminate ronco altogether.
By taking the condition seriously and seeking appropriate help, individuals and their families can look forward to better sleep, improved health, and a more peaceful environment. Whether it’s a lifestyle adjustment or a medical treatment plan, addressing ronco early can make a significant difference.